Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body and plays a crucial role in the structure and elasticity of our skin, bones, tendons, and muscles. The production of collagen depends on various vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients. Here are the main cofactors and their functions:
1. Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
Function:
✔ Vitamin C hydroxylates proline and lysine → this stabilizes collagen fibers.
✔ Protects collagen from breakdown (strong antioxidant).
✔ Essential for the production of collagen in our skin, bones, and tendons.
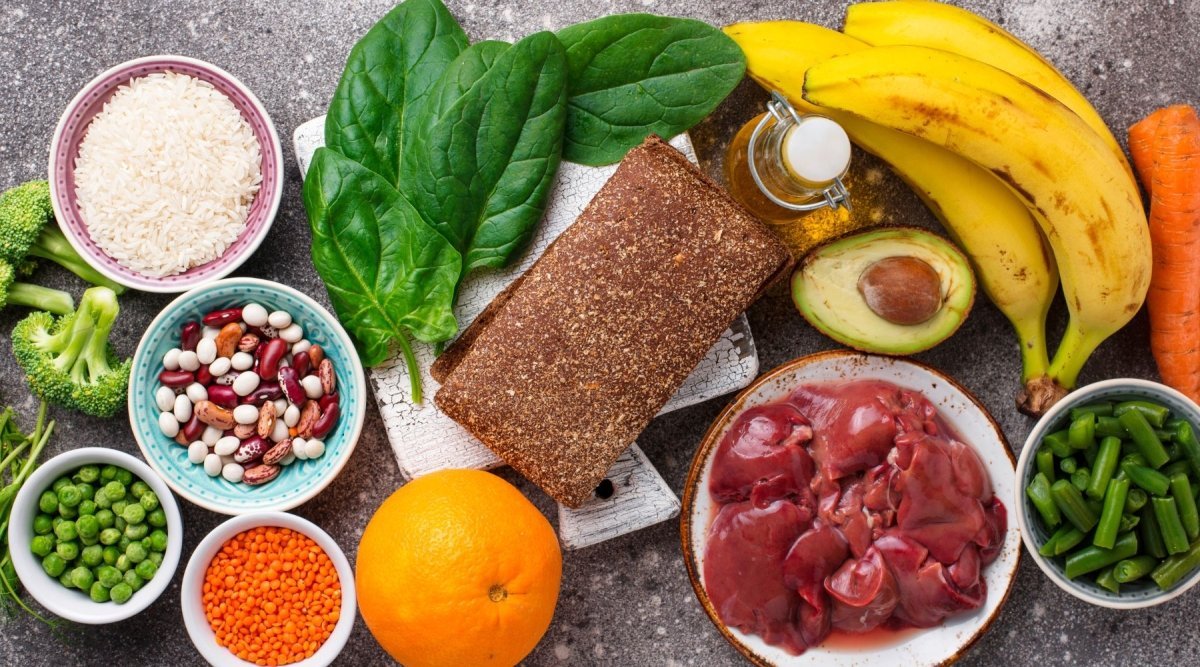
Sources: Berries, citrus fruits, bell pepper, kiwi (rich in vitamin C) & Camu Camu: The Vitamin C Champion from the Amazon region
2. Vitamin A (Retinol)
Function:
✔ Stimulates fibroblasts (cells that produce collagen).
✔ Ensures faster wound healing and structure and elasticity of the skin.
✔ Prevents collagen breakdown due to sun exposure.
Sources: Liver, eggs, dairy (rich in vitamin A). Why is Vitamin A (retinol) so important? read more about it in this blog.
3. Copper (Cu)
Function:
✔ Activates lysyl oxidase, which links and strengthens collagen fibers.
✔ Needed for the production of elastin, which keeps the skin supple.
Sources: Liver, oysters, red meat.
4. Zinc (Zn)
Function:
✔ Stimulates fibroblasts and enzymes that produce collagen.
✔ Supports wound healing and repair of our skin.
✔ Protects collagen against oxidative damage caused by sun exposure.
Sources: Oysters, red meat, pumpkin seeds, nuts, egg yolk.
What exactly is collagen?
Chemical Composition of Collagen
Collagen occurs in various structures in the body and mainly consists of amino acids, with a high concentration of glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. This contributes to the strength of bones, muscles, tendons, and cartilage.
Complete Amino Acid Composition of Collagen
Here is an overview of the main amino acids in natural collagen and their functions:
- Amino acid% in CollagenFunctionGlycine~33%Stabilizes the triple-helix structure.
- Proline~12%Provides strength and stiffness
- Hydroxyproline~10%Unique to collagen type, strengthens structure
- Alanine~11%Helps with structure and elasticity
- Arginine~4-5%Supports wound healing and nitrogen balance
- Glutamine~4%Important for cell repair and gut health
- Hydroxylysine~1%Connects bones and muscles through crosslinks
- Leucine~3%Involved in muscle building and recovery
- Valine~2%Helps with muscle recovery and collagen production
Why is this important?
✔ Collagen is found in bones, muscles, tendons, and cartilage, and determines their strength and flexibility.
✔ The variety of amino acids makes collagen functional for different tissues.
✔ As you age, the amount of collagen in the body decreases, which can lead to less elasticity in the skin and joints.
Water (~5-10%)
Water plays a crucial role in the structure and elasticity of collagen:
✔ Hydration: Water molecules bind to collagen and influence its mechanical properties.
✔ Structure: The interaction between water and collagen determines the strength of the collagen network.
Minerals (trace amounts)
Although minerals are present in smaller amounts, they are essential for the stability and production of collagen:
✔ Calcium and Phosphorus: Important for the mineralization of bones and tendons.
✔ Zinc and Copper: Help enzymatic processes that build collagen and protect against oxidative damage. Curious if your zinc levels are adequate? learn more about the symptoms of zinc deficiency.
How to naturally supplement collagen?
Because collagen production decreases as we age, it can be useful to obtain extra collagen from food or supplements.
Food sources rich in collagen:
- Bone broth – contains a type of collagen that is well absorbed.
- Fish and poultry – contain natural amino acids for skin, bones, and muscles.
- Eggs and dairy – contain proline and glycine for tendons and cartilage.
Collagen supplements:
- Collagen powder – a convenient way to supplement your daily collagen intake.
- Buying collagen? Choose a supplement rich in type 1 and 3 collagen for radiant skin and strong joints.
Conclusion
Collagen is an essential protein for our skin, bones, tendons, and muscles. By combining a diet rich in vitamin C, zinc, copper, and vitamin A with natural collagen sources or a collagen supplement, you can contribute to radiant skin, healthy joints, and strong connective tissue.
Want to support your collagen production? Everything about the best Collagen supplement can be read in this blog.
Choose natural nutrition (more about why organ meat is really healthy) and high-quality supplements to maintain the elasticity and firmness of your skin and joints!