The Wonders of Eggs: An In-Depth Look at Their Health Benefits
Eggs have been a nutritious and versatile part of our diet for centuries. Besides their delicious taste, they bring numerous health benefits. Let's take a thorough look at why eggs are so beneficial for our health.
Health Benefits of Eggs
High-Quality Proteins: Eggs are an excellent source of protein, with one egg containing about 6-7 grams of protein. These proteins contain all the essential amino acids our body needs to build and maintain muscles, tissues, and enzymes.
Essential Vitamins and Minerals: Eggs are rich in various important nutrients, including vitamin B12, which is essential for a healthy nervous system, vitamin D for strong bones and teeth, and vitamin A, which is good for the skin and eyesight. Additionally, eggs contain iron, phosphorus, and selenium.
Good Fats: Although eggs contain some cholesterol, studies have shown that the impact on blood cholesterol levels is limited. Moreover, eggs contain omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for the heart.
Protein Content and Nutrients in Eggs
One egg contains about 6-7 grams of protein, depending on the size. Besides proteins, an egg contains essential nutrients, including:
- Vitamin B12
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin A (retinol)
- Iron
- Phosphorus
- Selenium
Quality of Eggs
When buying eggs, it is important to pay attention to the following points for the best quality:
Origin and Labels: Preferably choose eggs from free-range hens or organic eggs. These often come from hens that have had a healthier diet and more space to roam.
Freshness: Check the expiration date on the egg carton. Fresh eggs generally have a thick consistency and a round yolk that stays firmly in place.
Eggshell Color: The color of the eggshell does not affect the nutritional value. Brown eggs come from brown hens and white eggs from white hens. The difference is only in the genetics of the hen.
The Importance of Egg Yolk
Choline:
Choline is an essential nutrient involved in the formation and maintenance of cell membranes.
It also plays a crucial role in brain development, especially during pregnancy.
Lutein and Zeaxanthin:
These antioxidants belong to the carotenoids and are important for eye health.
They help reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and cataracts.
Vitamin D:
Vitamin D is essential for maintaining strong bones and teeth, but it is not abundantly present in many foods.
Egg yolk is one of the few natural dietary sources of vitamin D.
Vitamin A:
Vitamin A is important for skin health, the immune system, and vision.
It is converted in the body from beta-carotene, which is also present in egg yolk.
Fats:
Although egg yolk contains fat, they are mainly monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which are considered healthy.
These fats are important for the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, including vitamins A, D, E, and K.
Iron and Phosphorus:
Egg yolk also contains important minerals such as iron, essential for oxygen transport in the body, and phosphorus, important for the formation and maintenance of bones and teeth.
Eggs Are a Valuable Addition to the Diet
Although the yolk contains cholesterol, it is important to note that nutrition experts generally state that moderate egg consumption does not have a significant effect on cholesterol levels in healthy people. In fact, the yolk provides a concentrated source of nutrients that contribute to various aspects of health, including brain function, vision, and the immune system.
By consuming eggs whole, one maximizes the benefits of the various nutrients present in both the egg white and the yolk, contributing to a balanced diet and optimal health. So stop following the "lean bro ideology" by throwing away yolks and only eating the egg white.
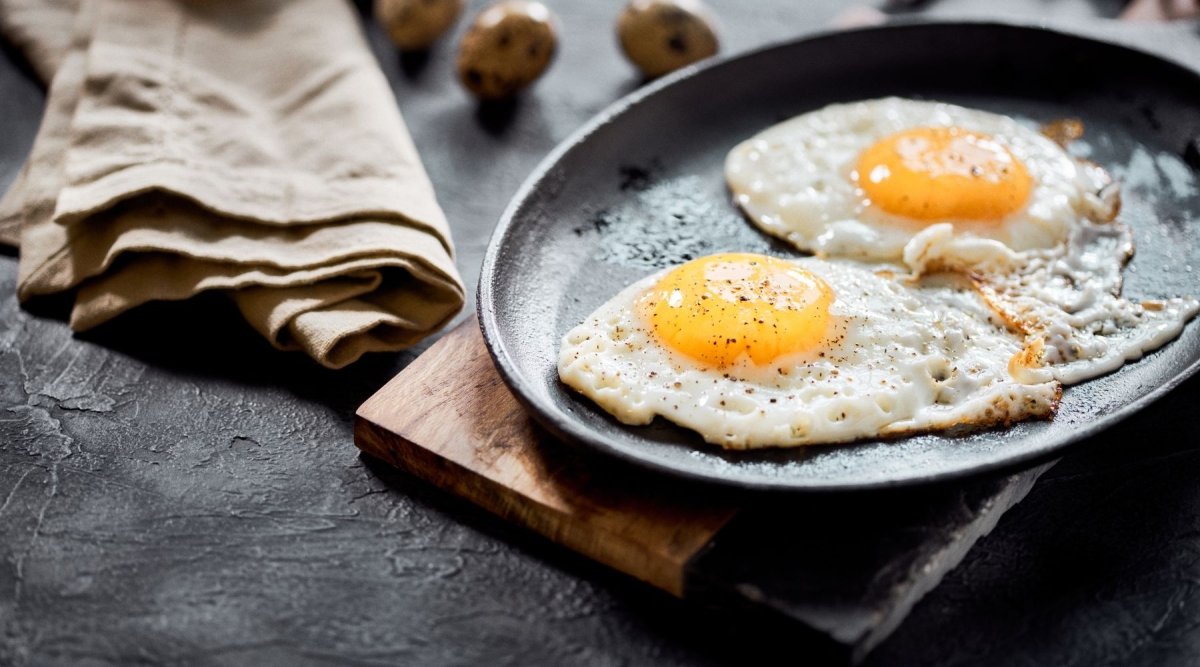
The color of the egg yolk
The color of the egg yolk usually varies from light yellow to deep orange, depending on the chicken's diet. The difference in color is related to the types of pigments the chicken absorbs through its food. Generally, a diet rich in certain nutrients can influence the color of the egg yolk.
Xanthophylls and Carotenoids:
Chickens fed diets rich in xanthophylls and carotenoids, such as beta-carotene, generally have darker, orange egg yolks.
Orange egg yolks often indicate a higher content of carotenoids, such as lutein and zeaxanthin, which are good for eye health.
Corn and Alfalfa:
Chickens that have corn and alfalfa in their diet often produce yolks with a more intense yellow color. This is because corn and alfalfa naturally contain carotenoids.
Omega-3 fatty acids:
Chickens fed with feed rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as flaxseed, can produce yolks with a deeper, orange color.
Both yellow and orange yolks can still contain a similar amount of nutrients, depending on the chicken's overall diet. However, the type of food the chicken consumes can affect specific nutrients, such as carotenoids.
In general, a deeply colored yolk often indicates a more varied diet for the chicken, possibly with a higher content of certain nutrients that are beneficial for health. But it is important to note that the color of the egg yolk alone does not necessarily reflect the nutritional value.
Where do I buy my eggs?
The best quality eggs you buy from the local farmer. Always ask the farmer about the living and feeding standards of the chickens. A real highlight in the Netherlands are the orange chicken eggs sold by zorgnatuur. Chickens that eat grass and insects and have optimal freedom of movement, which makes the quality of the egg the most favorable.